What are the causes of Brain Stroke?
Brain strokes, also known as strokes, occur when the brain's blood flow is disturbed, causing brain cell injury.
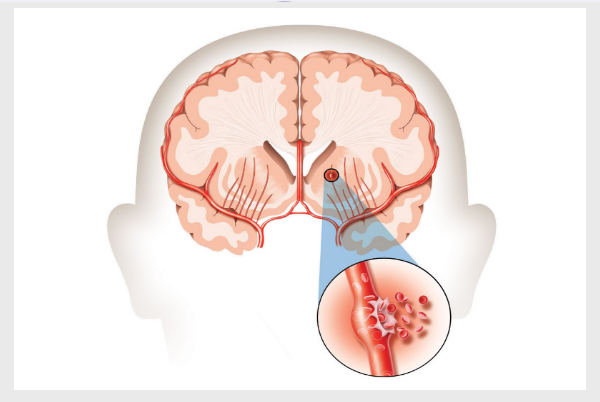
In reality, a stroke is a serious medical emergency that needs quick treatment. The blood needs to flow regularly in brain arteries, but if the blood which flows to the brain is restricted or disrupted, whether by a clot or a burst in the blood vessel. Very soon, the brain cells get exhausted of oxygen and nutrients and later begin to die within minutes. You need to quickly rush to the hospital for treatment for survival.
The necessity of immediate first aid after a stroke cannot be neglected. Recognizing the signs and symptoms of a stroke, the patient should get emergency medical attention right away so that it will make a big difference in the chances of saving the patient and having better outcomes. The abbreviation "FAST" is frequently used to help detect stroke symptoms.
What are the symptoms of Brain Stroke?
B- Loss of Balance: Can’t stand properly, feels unconscious.
E - Blurred vision: Feeling blurred vision in eyes.
F: Face drooping: It means a portion of your face loosening or numb.
A: Arm weakness: One arm gets weak for raising the hand even
S: Speech difficulty: It means speech is affected while talking or difficult to understand.
T: Time to call emergency services: If any of these signs are observed, it's crucial to call for emergency medical help immediately.
Early diagnosis in critical situations helps to handle every complication of severe brain injury. It depends on the kind of stroke; emergency medical experts can administer clot-busting drugs or perform clot removal treatments.
Post-stroke treatments help in a variety of strategies that result in many complications of recovery, including regular medical treatment and management for the patient's recovery. Rehabilitation attempts to remind the person to regain the abilities that he has lost and let him adapt to the new way of functioning. A patient can recover from a stroke through essential practices like physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy.
Educating oneself and others about the indications of a stroke and following a healthy lifestyle to lower the risk of strokes, as well as learning what to do and how to respond in the situation of a brain stroke would help save someone's life. Taking proper measures on time will not only save the lives of the people but will also help them recover and have a higher quality of life ahead.
Here are two types of stroke: Ischemic and Hemorrhagic
It has several causes:
Ischemic Stroke:
Thrombotic Stroke is caused by a blood clot (thrombus) forming in one of the arteries that feed blood to the brain.
Embolic Stroke occurs when a blood clot or debris originates somewhere in the body (often in the heart) and travels to the brain, producing a blockage in smaller arteries.
Hemorrhagic strokes:
Intracerebral haemorrhage is caused by the sudden bursting or breaking of a blood artery within the brain, resulting in bleeding and injury.
Subarachnoid haemorrhage: Bleeding in the gap between the brain and the surrounding membrane, usually caused by a burst aneurysm.
Common causes and risk factors for stroke:
Hypertension (high blood pressure): high blood pressure weakens blood vessel walls, making them more close to bursting or stopping them from moving.
Atrial fibrillation: An irregular heart rhythm increases the risk of blood clots in the heart travelling to the brain.
Smoking: Tobacco smoking causes arterial hardening, which increases the risk of blood clots.
Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels, increasing the risk of a stroke.
High cholesterol: High cholesterol levels can cause plaque accumulation in the arteries, decreasing blood flow to the brain.
Age: The risk of a stroke rises with age, particularly after 55.
Family: A family history of stroke, or a specific genetic one, may increase the risk.
Gender and Race: Men are at a higher risk than women, and particular races, such as African Americans and Hispanics,.
Prior Stroke or Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): Having a stroke or TIA raises the risk of having another one.
Poor Diet and Physical Inactivity: An unhealthy lifestyle leads to obesity and cardiovascular disease, which increase the risk of stroke.
Myth and Reality about Brain Stroke
Que. Stroke is not preventable?
Ans. No, up to 80% of strokes are.
Que. Stroke cannot be treated?
Ans. No, it requires emergency treatment.
Que. Does stroke only strike the elderly?
Ans. No, anyone can have a stroke.
Que. Does a stroke happen in the heart?
Ans. No, a Stroke is a "Brain attack".
Que. Does stroke recovery end after 6 months?
Ans. No, Stroke recovery can last a lifetime!