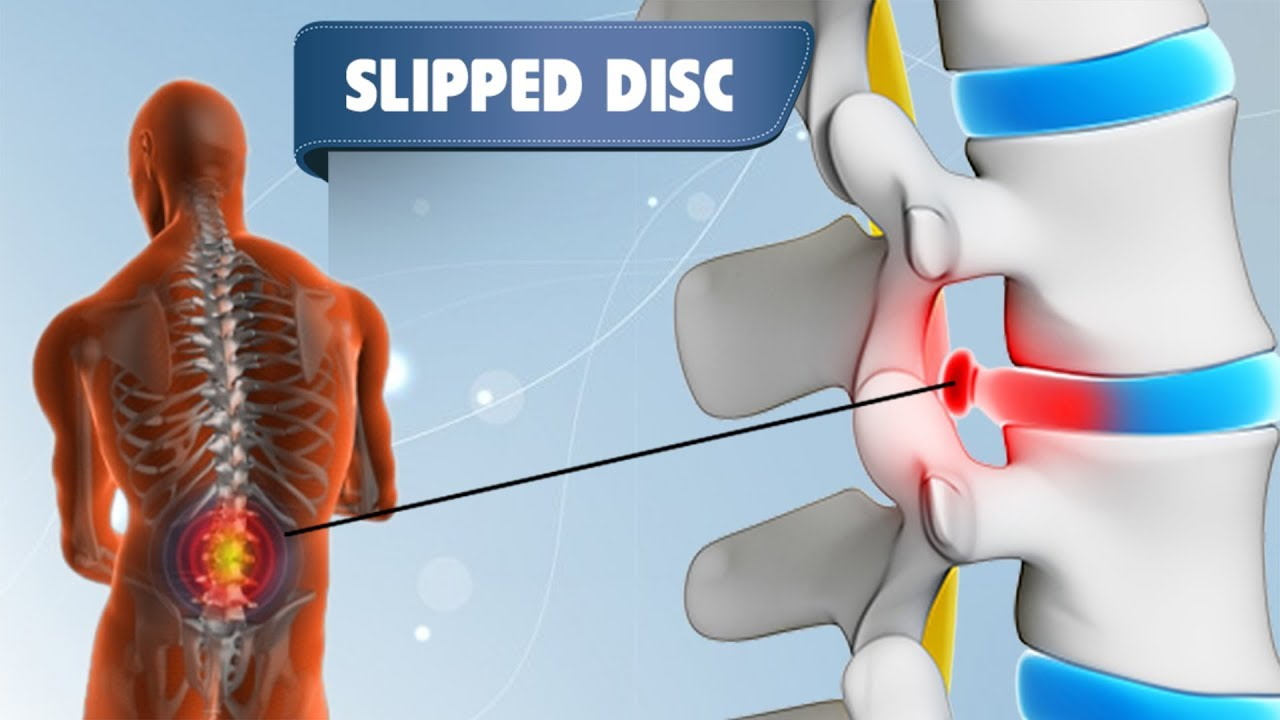
What is a slip disc?
A slipped disc is a type of disorder in which a spinal disc stands out, potentially putting pressure on the root of the nerve that emerges from the spinal cord. This occurrence will cause a variety of uncomfortable symptoms, and it will be found to be most common in many people. A slipped disc is characterized by muscular weakness, trouble walking, burning sensations, and discomfort, which can have a substantial influence on one's quality of life.
Surgical surgery and medication are the only choices for patients who bear the pain of a slipped disc. The surgical method tries to relieve pressure on damaged nerves; hence, you see a reduction in symptoms in the body. Drug therapies may include pain management—that is, how to reduce slipped disc pain—and using anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce the inflammation and discomfort related to your body pain.
While surgical alternatives are considered in extreme instances or when traditional therapies fail, early identification and a thorough knowledge of the symptoms and causes are critical for optimal care. Seeking medical advice is critical for developing personalized treatment regimens that allow patients to regain control of their daily activities and have a higher quality of life despite the limitations offered by a slipped disc.
Symptoms of SLIPPED DISC:
-
Muscle Weakness: Impaired Strength: Nerve compression can lead to diminished muscle function, resulting in weakness.
-
Difficulty in Walking: Challenges in Mobility: Coordination issues and discomfort while walking, indicating potential nerve compression.
-
Burning Sensation, Aching: Nerve Irritation: The presence of a burning sensation or aching may point to irritation of nerves associated with the slipped disc.
-
Pain in One Side of the Body: Unilateral Discomfort: The discomfort is often localized to one side of the body and may radiate along the affected nerve pathways.
-
Numbness in Body: Loss of Sensation: Nerve compression can result in numbness, causing a lack of sensation in the affected areas.
-
Pain When Standing and Sitting: Position-Related Discomfort: Experiencing pain when standing or sitting, highlighting the impact of specific positions on the slipped disc.
Causes of SLIPPED DISC:
-
Bad Posture: Incorrect Spinal Alignment: Poor posture contributes to abnormal stress on spinal discs, increasing the risk of disc issues.
-
Smoking: Disc Degeneration: Smoking is linked to reduced blood flow to spinal discs, accelerating degeneration and heightening susceptibility to a slipped disc.
-
A lot of Sitting & Lifting: Prolonged Sitting: Extended periods of sitting contribute to spinal stress, while improper lifting techniques can strain the discs, predisposing them to herniation.
-
Overweight: Excess Weight Straining the Spine: Obesity places additional stress on spinal discs, increasing the likelihood of disc displacement and subsequent issues.
-
Increasing Age (Becoming Older): Natural Wear and Tear: Over time, the spine undergoes natural degeneration, leading to wear and tear on spinal discs. Ageing is a key factor in the development of slipped discs.
5 Types of Disc Degeneration:
-
Normal Disc: Healthy Spinal Structure: The spine maintains its standard disc structure without any signs of degeneration or abnormalities.
-
Degenerative Disc: Gradual Wear and Tear: Over time, discs undergo natural degeneration, resulting in reduced flexibility and shock absorption. This process is part of the ageing of the spine.
-
Bulging Disc: Disc Protrusion: The disc extends beyond its normal boundaries, potentially pressing on nearby nerves. This protrusion can cause discomfort and other symptoms.
-
Herniated Disc: Disc Rupture: A more severe condition where the disc's outer layer ruptures, leading to the leakage of the inner disc material. This can result in nerve compression and various symptoms.
-
Thinning Disc: Reduced Disc Height: The disc loses its normal thickness, impacting spinal support and potentially contributing to instability and discomfort.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an awareness of the symptoms along with the signs and indicated in daily routine activities with a slipped disc is essential for preventive therapy and better spinal health. Early detection is the core of effective enforcement, directing healthcare practitioners to use specialized diagnostic techniques and treatment strategies. Seeking medical counsel as soon as symptoms appear is critical to providing complete care and prompt relief of discomfort, therefore restoring normal performance.
Additionally, being aware of the activities related with slip disc, such as bad posture, lifestyle choices, and age-related wear and tear, emphasizes the necessity of taking preventative measures. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, keeping good posture, and avoiding sedentary habits or poor lifting techniques are critical steps toward sustaining spinal health. Regular exercise, weight control, and timely medical intervention for long-term pain all contribute to overall spine health, lowering the chance of disc disorders.
Understanding the various forms of disc degeneration improves one's capacity to identify and treat spine-related issues. If symptoms are not treated promptly, they may intensify. Consultation with a healthcare practitioner is recommended to decide the best course of action, whether conservative measures such as physical therapy and drugs or advanced procedures, including surgical possibilities, depending on the severity of the problem. Prioritizing spine health via educated decisions and immediate attention improves long-term well-being.